There are several methods for examination of the brain by imaging. The choice of method depends on which part of the brain is being examined. The most common methods are described below.
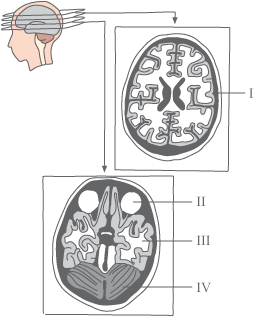
I: Cerebral hemisphere
II: The eyes
III: Cerebral hemisphere
IV: Cerebellum
CT scan of the brain producing multi level
cross-sectional images of the brain showing the
different structures of the brain
CT-scan - Computer Tomography
A CT scanner uses X-rays to create images of thin sections of the brain and skull. The patient lies on a stretcher with the head inside the CT scanner, which sends X-rays through the brain from all possible angles. A computer collects all the information and creates a series of cut images of the brain. Most structures in the brain become visible. In particular CT scans are used to diagnose blood clots or heamorrhage/bleeding in the brain and brain tumors. Abnormal areas in the brain where damage has occurred will be either whiter or darker than normal brain tissue.
The CT scan can be combined with contrast fluid injected into the blood vessels. If the contrast accumulates in a particular area this is a sign of bleeding from a damaged blood vessel or other damage involving leaking.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance)
Magnetic resonance imaging – MRI or MR scan is a valuable diagnostic method introduced in the early 1980’s.
The MRI scanner exploits that the body's hydrogen atoms behave like little magnets with a south and a north pole. The MR scanner consists of an electromagnet, a radio transmitter, a receiver and a computer. During the scan, the head is placed inside the scanner's magnetic field. Normally the body’s hydrogen atoms point in different directions but the scanner’s powerful magnetic field causes the hydrogen atom protons to align themselves in the same direction. Then radio waves are transmitted through the head, which knock the protons out of alignment. When the radio wave is cut the atoms realign and when doing so emit tiny signals which are picked up by the receiving magnet and passed on to the computer where the signals are processed and the image created. Areas with much fluid (water) contain many hydrogen atoms and will give a strong signal. The image thus expresses the difference in water content in different tissue.
The MRI provides a very detailed image of brain tissue and is particularly good for diagnosing multiple sclerosis. Often the scan is performed with the use of a specific contrast agent that shows damage to blood vessels and the blood-brain-barrier (see also Brain). In addition, the MR gives a better image of the lower rear part of the brain. One advantage of MRI is that the patient is not exposed to ionizing radiation (X-rays) as by the CT scan. MRI cannot be used if the patient has metallic parts in the tissue. Patients with a claustrophobic tendency might have problems with lying in the scanner which is a very narrow tunnel.
Angiography
Angiography is a procedure where blood vessels can be shown clearly on X ray films for diagnose of malformation of the brain's blood vessels such as aneurisms ( ballooning of an artery) and narrowing or blockage of blood vessels by atherosclerosis or thrombosis. Angiography can be made by the introduction of a contrast agent into a vein, usually in the neck, followed by a series of X-rays where the contrast is followed during its passage through the blood vessels. In another procedure a special MRI is performed which produces a very clear image of the veins in the brain. This method avoids the administration and complications of injecting a contrast medium and is used increasingly.
PET scanning - Positron Emission Tomography
A Positron Emission Tomography or PET scan can detect a slightly radioactive tracer, which is injected into a vein in the arm. The radioactive tracer is absorbed mainly in the areas of the body with high metabolism. This is visible in tumors and the PET scan is widely used in cancer treatment. Also changed metabolism in areas of the brain affected by epilepsy can be observed with this method . In addition, the PET scan is extensively used in research of various brain diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia and depression.
SPECT scans (Single Photon Emission Computer Tomography)
SPECT scan is used to map the brain's blood flow. A slightly radioactive tracer is injected into the bloodstream followed by the brain scan. A so-called gamma camera is used which measures the amount of radiation as a reflection of the bleeding intensity in the various areas under examination SPECT scan is for example used to diagnose epilepsy, memory problems, migraine and Parkinson's disease.
Przeczytaj ten artykuł w języku polskim |